visual
Disasters and safety accidents have been becoming gradually larger
and more complex, leading to larger social and economic human
damage/loss.
Secuware applies IoT/ICT to disaster and safety sites,
provides support to secure quick and accurate response
power when large disasters occur, and also
provides solutions to protect safety and lives of people
from various disasters and safety risk factors.
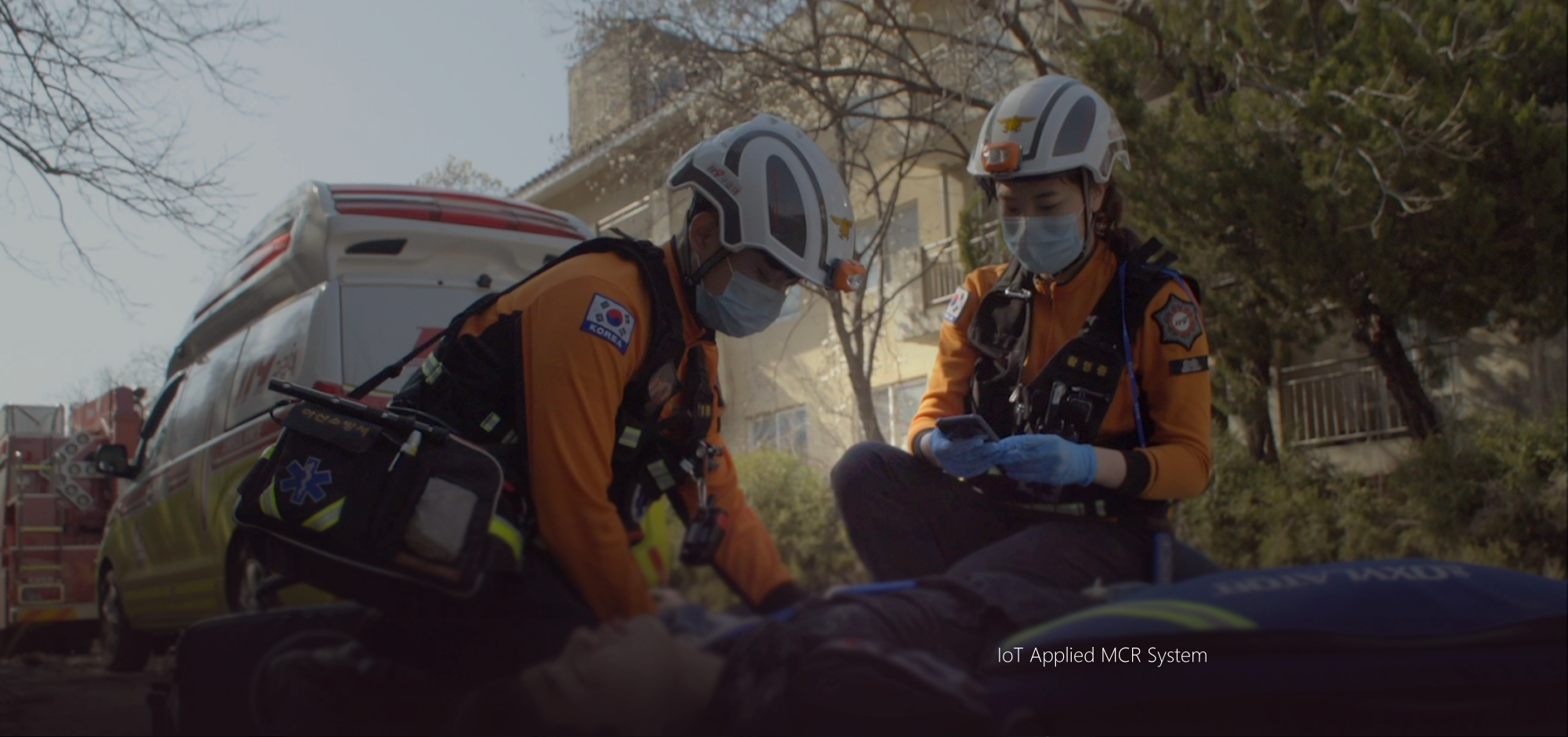
Casualty Response procedures
-
 On-Site Arrival The Emergency Service Workers arrived at fields classify severity of casualties quickly and accurately.
On-Site Arrival The Emergency Service Workers arrived at fields classify severity of casualties quickly and accurately. -
 Primary Classification At the fields, a Temporary Emergency Medical Care Station is installed, and the casualties whose severity was classified are moved to the Temporary Emergency Medical Care Station.
Primary Classification At the fields, a Temporary Emergency Medical Care Station is installed, and the casualties whose severity was classified are moved to the Temporary Emergency Medical Care Station. -
 Secondary Classification After installing the Temporary Emergency Medical Station, cooperation with relative institutions including the public health center and DMAT are performed. After which the secondary severity classification decide the transfer priorities.
Secondary Classification After installing the Temporary Emergency Medical Station, cooperation with relative institutions including the public health center and DMAT are performed. After which the secondary severity classification decide the transfer priorities. -
 Massive Casualty
Massive Casualty
Response System(MCR) Massive Casualty Response System(MCR) can share information of casualties at the fields in real-time with relative institutions for disaster response such as the public health center, DMAT, ,911 Emergency Service Workers, as well as other relevant disaster response agencies.
Problems in the disaster site
-
In 2016, a Five-car collision in Kangwon bongpyung tunnel let to 4 deaths and 37 injured.
-
Explosion at the subway construction site in Namyangju killed 4 people and injured 10.
-
Fire at Miryang city killed 32 with a casualty of 120.
-
A 21-car chain collision on the West Coast Highway, and 106-car collision.
Current problems in the disaster site are as follows:
1) Paper triage are used to record casualty information
2) Frequent calls between on-site workers and the situation room cause unnecessary work burdens on Emergency Service Workers
3) Inaccurate information on casualties is delivered to relative institutions, causing statistical errors.
4) Difficulties in tracking transported patients.
5) Transfers made without on-site severity classification can lead to patient capacity overflow in certain hospitals.
Related rules
Massive Casualty Response System(MCR) is developed in accordance with the law of Emergence Rescue Response Activitiesand used at disaster sites.
At disaster sites where time is of the essence, an app with severity classification algorithm can make a difference.
Activities and Field Command
[Enforcement 2018. 8. 30.]
[Ordinance of the Ministry of Public Administration and Security, Sub-paragraph 70, 2018. 8. 30., Partially revised]
rticle 22 (Roles of Classification Team)
① Article 20 The Classification Team in accordance with Article 20 (4) checks casualties occurred at disaster sites classifies them into four stages: Dead, immediate, priority and delayed based on states of casualties. (Revised April 3, April 30, 2015)
② The Classification Team shall have a doctor to check and classify casualties.
③ Three severity classification tables in Table 7 shall be attached to classified casualties. However, electronic devices to indicate, record and save severity classification information can replace the severity classification tables by attaching the device on their chest. In which case, it is necessary to show the saved casualty information using the device. <Revised Aug 30. 2018>
Article 24 (Roles of Transfer Team)
① The Transfer Team in accordance with Article 20 (4) secures or controls an ambulance/hearse to transfer casualties. The team must maintain close contact with medical institutions after receiving patients from the Classification Team and Emergency Medical Team. <Revised April 3. 2015>
② As for the transfer priority of casualties in accordance with Paragraph 1, immediate patients have highest priority, followed by priority, delayed, and the dead. <Revised April 3. 2015>
③ The Transfer Team member transporting casualties shall submit the transfer status information written in No. 2 format without delay to the Transfer Team in accordance with Article 22 (3) and shall record and keep attached severity classification chart and medical reports. In this situation, the transfer team member transferring casualties shall keep a copy of severity classification table while handing over two copies to the transfer team leader and the hospital of transfer. <Revised April 3 2015, Aug 30. 2018>
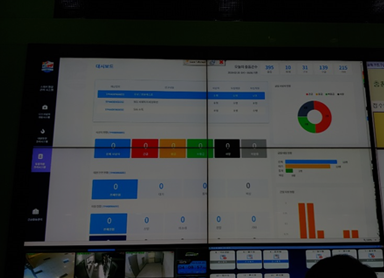
System overview
E-Triage system makes it possible to view on-site medical team’s severity classification process/decision and transfer situation in real-time at the situation room, field command center, and transport awaiting hospitals.


Backbone network failure frequently occur during large disasters.
In this situation, our Mass Casualty Response System establishes it’s own private networking system. MCR continues to communicate casualty information to the on-site commander’s command device. When the telecommunication network is recovered, the information collected using MCR network are delivered to the server.
Product Configuration
Massive Casualty Response System (MCR) - Management system 'e-Triage' and 'e-Triage Tag' - on-site casualty classification software
'USB LoRa Gateway' – Able to connect to any device including the ‘hybrid e-Triage system’
Massive Casualty Response System(MCR)
Web-based Massive Casualty Response Control System
The transfer priority is displayed by classifying severity of casualties quickly and accurately using the e-Triage casualty severity classification algorithm. The e-Triage Tag displays severity states as colors, GCS, and RTS score. It is possible to manage and check these information on the Massive Casualty Response System(MCR) server.
The Massive Casualty Response System provides information on casualty status, casualty details, hospital capacity, transfer hospital information, statistics, and information management features.
The severity classification is made by inputting Glasgow Coma Scale(GCS), respiration rate per minute, and blood pressure information. Results are displayed as colors on the e-Triage Tag and it is possible to manage and check on the Massive Casualty Response System(MCR) server.
Information on casualties, injuries & treatments, severity classification, status of patient transfer hospitals is saved on the Massive Casualty Response System(MCR) server.
Number of casualties, casualty severity results, and transfer information can be acquired using the e-Triage system.
Hospitals can prepare for incoming patients in advance using patient information.
One e-Triage tag will be worn per patient. The tag will display colors, GCSs, and RTS score based on patient’s severity.
e-Triage inputs Glasgow Coma Scale(GCS), respiration rate per minute, and blood pressure information and inputs them into a proportionally increasing point-value classification system. The results are then relayed to e-Triage tags.
e-Triage Tag updates(changes) color when patient severity changes.
e-Triage
Casualty Severity Classification Application (iOS, Android)
Product Description
Casualty information is input in real-time at disaster sites using a smart phone application(Software). In addition, it is possible to see objective and accurate information on the casualty status at disaster sites in real-time by using severity classification algorithm.
It is possible to add new severity classification features. (Pre-KTAS)
e-Triage
Casualty classification using various severity classification algorithms
Included infectious disease classification algorithms
Links with Emergency Activity Report Data
transfer information input feature & Favorites feature of transfer hospitals
Primary and Secondary classification
Real-time updates of casualties
Management of transfer status and hospital capacity
Management of self-escape status
Android, IOS
e-Triage Tag
NFC, LoRa. IoT-based RFID Tag
Features of the e-Triage Tag
Severity of casualties is displayed using LED.
Transfer priority management by displaying GCSs and RTS score.
Available to use online and offline using the Hybrid-Triage Tag.

Specifications of the e-Triage Tag
- Size: 101x63x13mm
- Data Receipt: NFC
- Dustproof/Waterproof grade : IP67
- Weight: 61g
- Data Transmittance: Lora
- Battery Life: 8~15 hours
- Operating temperature: -20℃ ~ +60 ℃
- Operating Voltage: 3.0V~4.2V
- Certification: KC
USB LoRa Gateway
Casualty information is collected using the
e-Triage Tag by constructing private network
when the backbone network fails. 
RF frequency: 922.1 ~ 923.3MHz (RF Module)
TX Power : Under 25mW(+14dBm)
RF Modulation: LoRa(5.4 kbps, SF7, BW125kHz) Sensitivity : -123dBm@PER 1%
Features of transmitting/receiving LoRa data
Features of receiving multiple LoRa data(1:N)
Transmitting/receiving LoRa data through the USB port
Available to use the Hybrid e-Triage System by connecting Windows Host Devices
(Tablet, Laptop)
Hybrid e-Triage System
Software for Windows-based Host Devices
Casualty information is collected and managed in the Hybrid e-Triage System in real-time when backbone network (3~5G, LTE, Wi-Fi, etc.) is disconnected due to disasters (offline state)
The Hybrid e-Triage System collects and manages casualty information received from the Hybrid-Triage Tag in real-time.
When telecommunications network is recovered, casualty information is sent to the MCR System Sever at the headquarters from the Hybrid e-Triage System.
Casualty information can be collected and managed even if internet is not available in some areas of disaster sites (Communications network failure state). The e-Triage Tag transmits casualty information to the Hybrid e-Triage system. One e-Triage tag will be worn per patient. The tag will display colors, GCSs, and RTS score based on patient’s severity. e-Triage inputs Glasgow Coma Scale(GCS), respiration rate per minute, and blood pressure information and inputs them into a proportionally increasing point-value classification system. The results are then relayed to e-Triage tags. e-Triage Tag updates(changes) color when patient severity changes. Hybrid e-Triage System can create temporary disaster numbers, import existing disaster information, and check information of hospital transfer status of patients. When the Internet(backbone network) is restored, Hybrid e-Triage System transmits the stored casualty information to the Massive Casualty Response System(MCR). Hybrid e-Triage System collects and manages the number of casualties for each severity, casualty information, results of the primary and secondary severity classification, and transfer information.
Cases of Backbone Network Collapse
- n March 2011, a magnitude 9.0 earthquake and tsunami in Japan led to collapsed telecommunication network and nuclear power plant reactor leak.
- In May 2014, a fire accident at Goyang bus terminal led to collapsed communication network.
- In November 2016, a large crowd gathered on weekends during a candle light rally in Gwanghwamun, South Korea collapsed the communication network.
- On Sep 28, 2018, a 7.5-magnitude earthquake near Sulawesi, Indonesia caused the tsunami, which collapsed the communication network.
- On November 24, 2018, a fire at the Ahyeon branch of KT telecommuncations company in Seodaemun district, Seoul, Korea collapsed the communication network
Massive Casualty Response System(MCR) can solve problems of sharing casualty information at disaster sites, problems concerning backbone network failure, in-transit communication for emergency room arrangement, and casualty severity priority visualization problems based on casualty classification results.
Patent & Certification Status


- Disaster Management System using electronic Triage (Patent)
Disaster Management System using the Hybrid Triage (Patent) - Massive Casualty Response System(MCR) GS Certification 1st class
Hybrid Triage System GS Certification 1st class
Institutions used
Institutions currently using:
Fire Department HQs, Fire Departments, 119 Safety Centers, Korean Coast Guards, Public Health Centers, Military (Medical Command), Hospitals
Registered as an Innovative Prototype by the Public Procurement Service
-
Composite
ProductsMassive Casualty Response System(MCR) Commodity Classification Code:99999920-24015194
-
Product
Configuration
InformationMassive Casualty Response Systemv1.0
(Massive Casualty Response(MCR) System) Commodity Classification Code: 43232902-23879342 -
Product
Configuration
Informatione-Triage v1.0
(Casualty classification using e-Triage: Android version) Commodity Classification Code: 43232902-23883804 -
Product
Configuration
Informatione-Triage v1.0
(Casualty classification using the e-Triage: iOS version on a smartphone) Commodity Classification Code: 43232902-23922588 -
Product
Configuration
InformationLTW2935-ETT (e-Triage Tag) Commodity Classification Code: 43221721-23731924
-
Product
Configuration
InformationLTC5102-ETC (e-Triage Tag and Charger) Commodity Classification Code: 26111704-23730976
-
Product
Configuration
InformationHybride-Triage Systemv1.0(Hybrid Unit: Self-network
construction system if the backbone network is not available) Commodity Classification Code: 43232902-23917682